One And A Half Syndrome Vs Ino

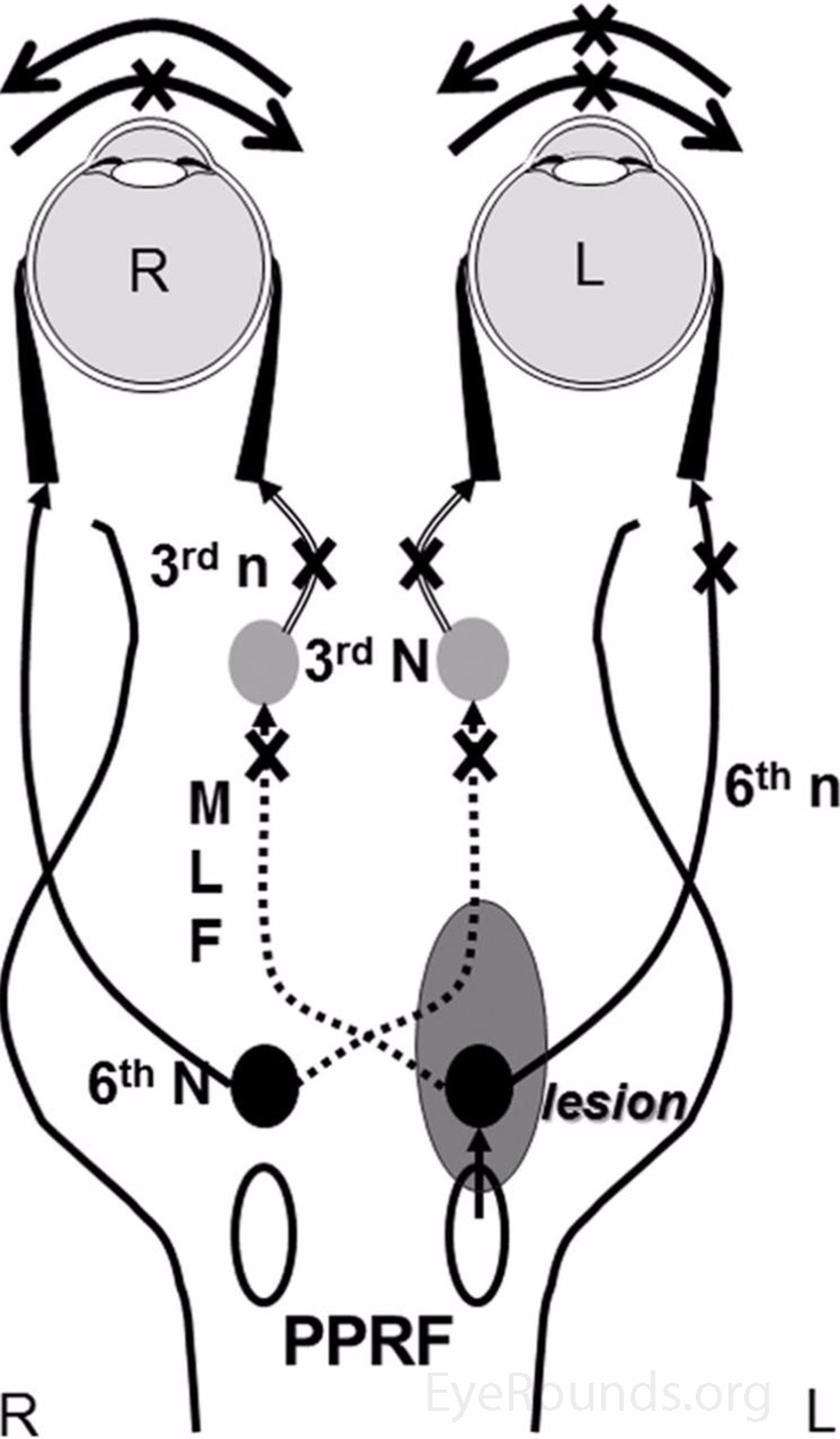
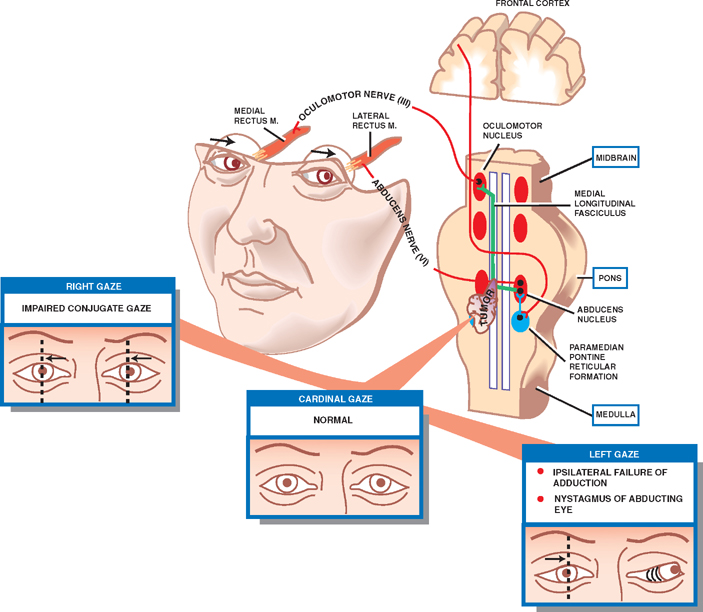
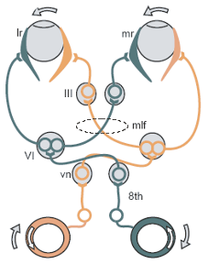
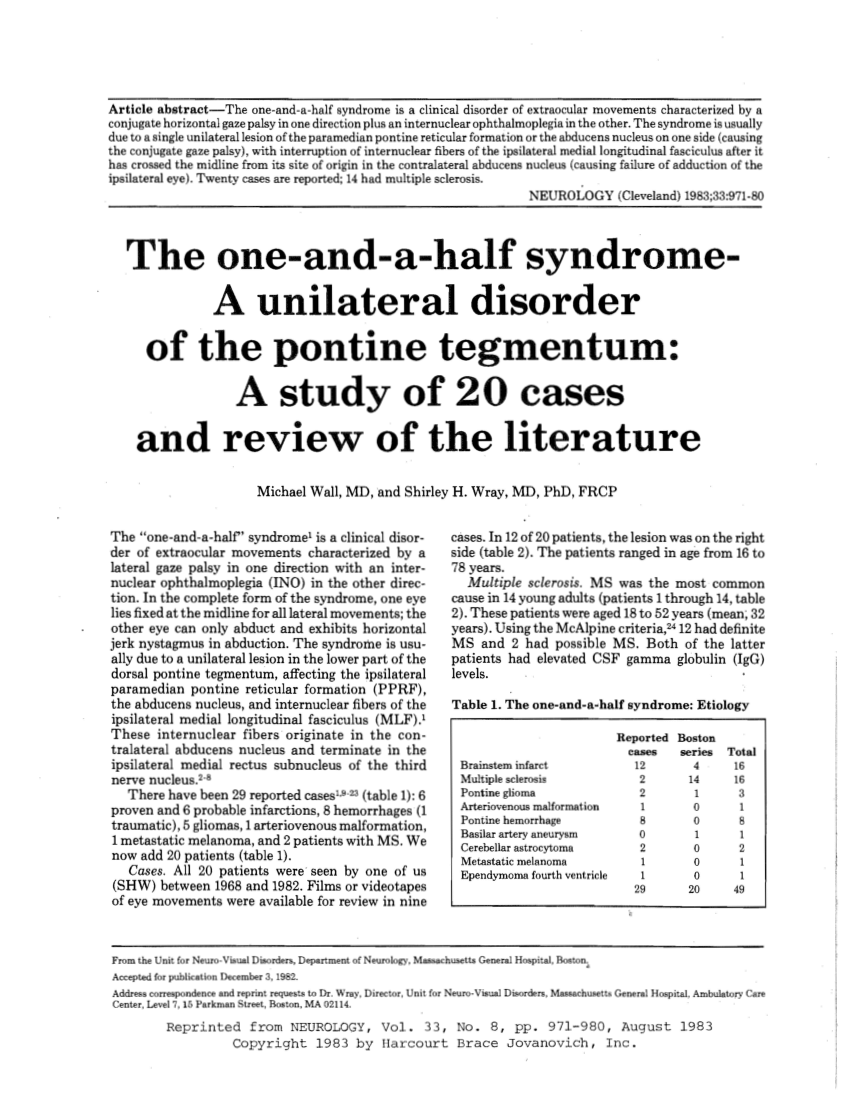
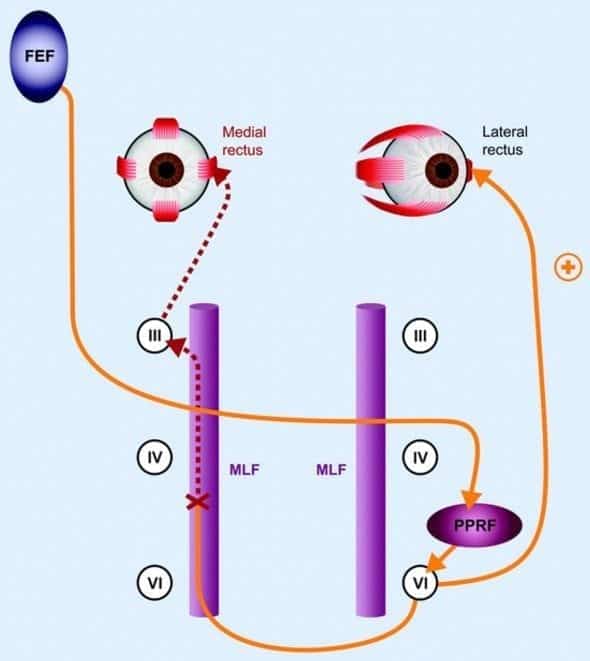
Pprf or the abducens nucleus and the mlf on the same side the mlf having crossed from the opposite side then the one and a half syndrome occurs with paralysis of all conjugate horizontal eye movements other than abduction of the eye on the opposite side to the lesion.
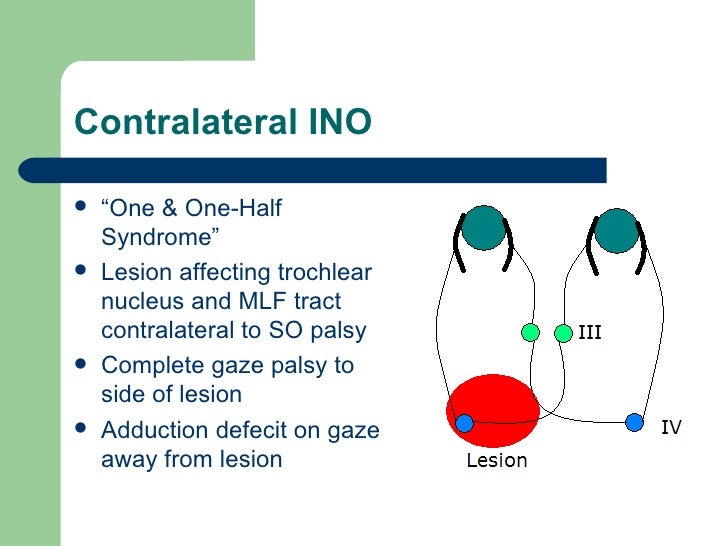
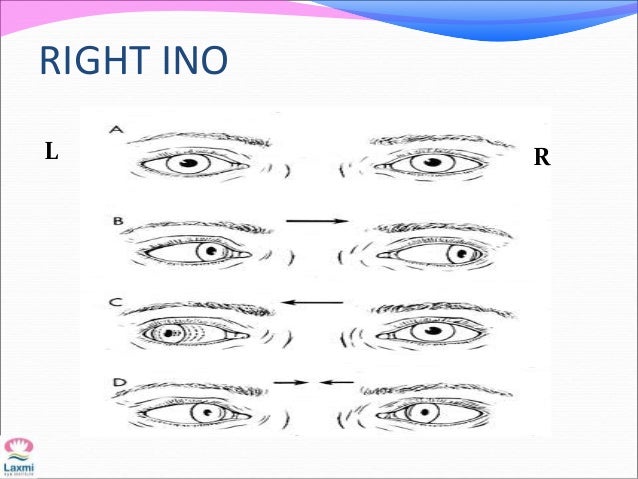
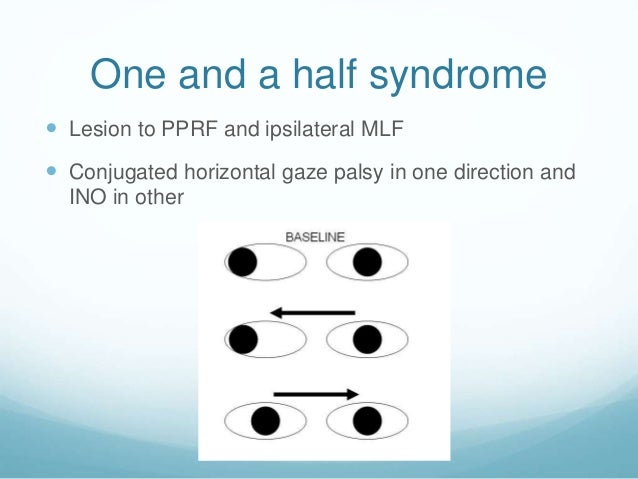
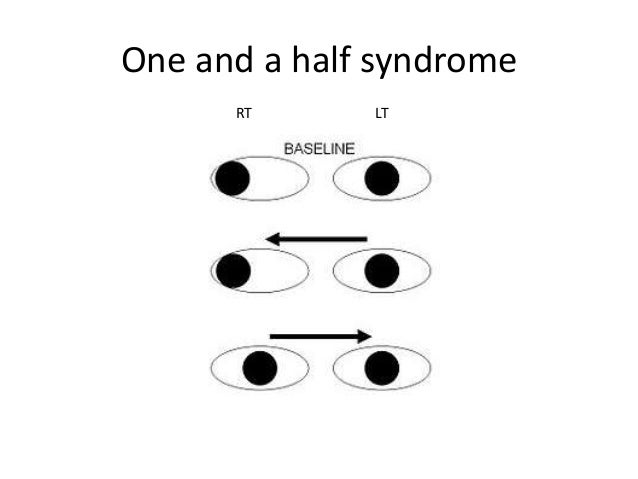
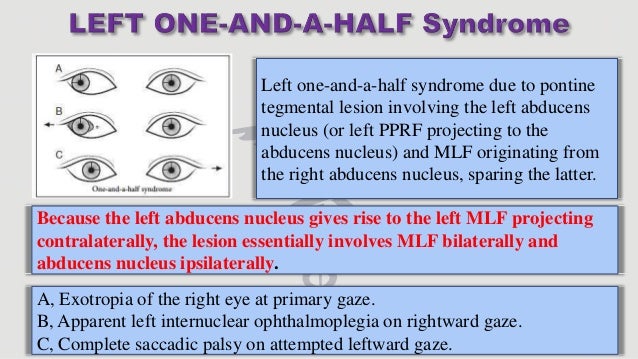
One and a half syndrome vs ino. A one and a half syndrome involves lesions of ipsilateral pprf or abducens along with ipsilateral mlf. 27 28 the ipsilateral abducens nucleus or pprf lesion results in an ipsilateral horizontal gaze palsy while the ipsilateral mlf lesion produces an ipsilateral ino with impaired ipsilateral adduction. Orthophoric or in acute stage ipsilateral eye esotropic or contralateral eye exotropic paralytic pontine exotropic. When an attempt is made to gaze contralaterally relative to the affected eye the affected eye adducts minimally if at all.
The contralateral eye abducts however with nystagmus. Additionally the divergence of the eyes leads to horizontal. Our patient had a combination of right ino and right facial nerve palsy with no other neurologic abnormalities a seven and a half syndrome. It presents a combination of ipsilateral conjugate horizontal gaze palsy one and ipsilateral internuclear ophthalmoplegia ino a half.
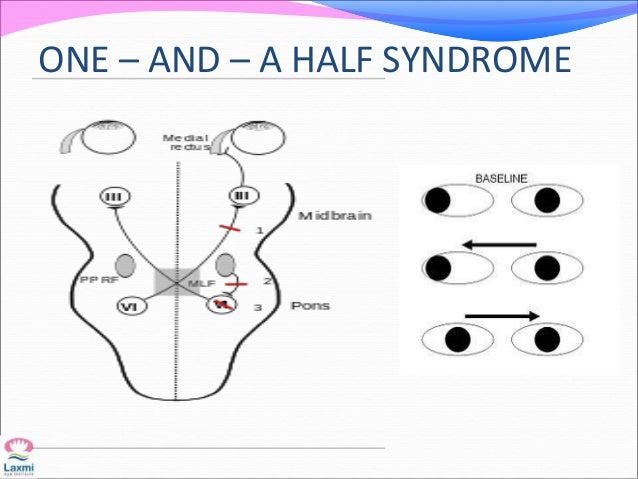
This is caused by a lesion that affects the ipisilateral paramedian. A concomitant cn viii palsy in this setting has been called the eight and a half syndrome. The only remaining horizontal movement is contralateral abduction. One and a half syndrome is a clinical disorder characterized by an ipsilateral conjugate horizontal gaze palsy the one and an ipsilateral internuclear ophthalmoplegia ino the half.
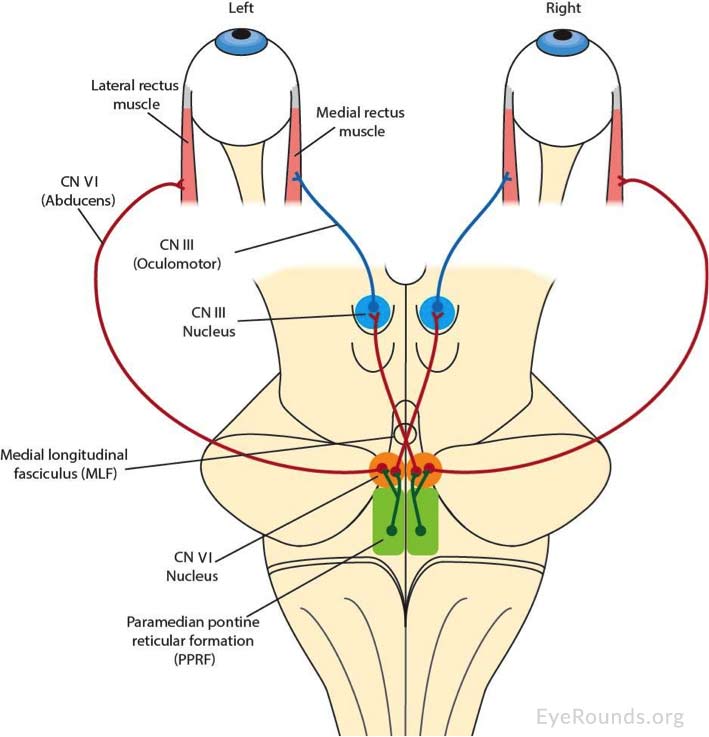
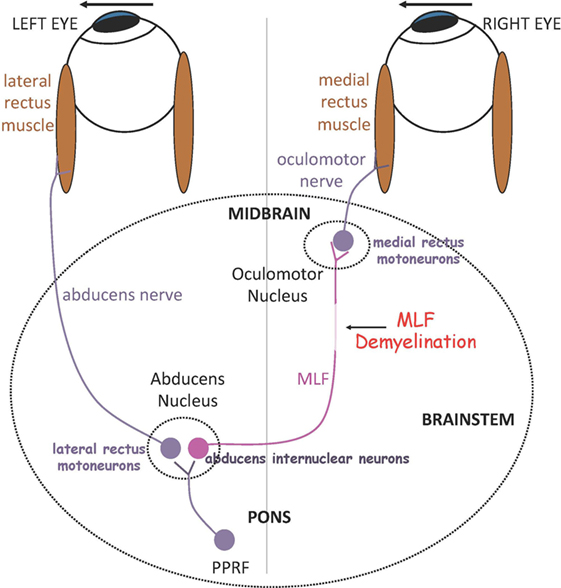
On the basis of the one and a half syndrome there are a series of related rare syndromes called the one and a half syndrome spectrum disorders. This manifests as one and a half of the horizontal eye movements being impaired with abduction of the contralateral eye being the remaining intact horizontal eye movement. An ipsilateral gaze paresis or palsy an internuclear ophthalmoplegia ino on contralateral gaze at rest the eyes are. Mlf syndrome internuclear ophthalmoplegia ino is a disorder of conjugate lateral gaze in which the affected eye shows impairment of adduction.
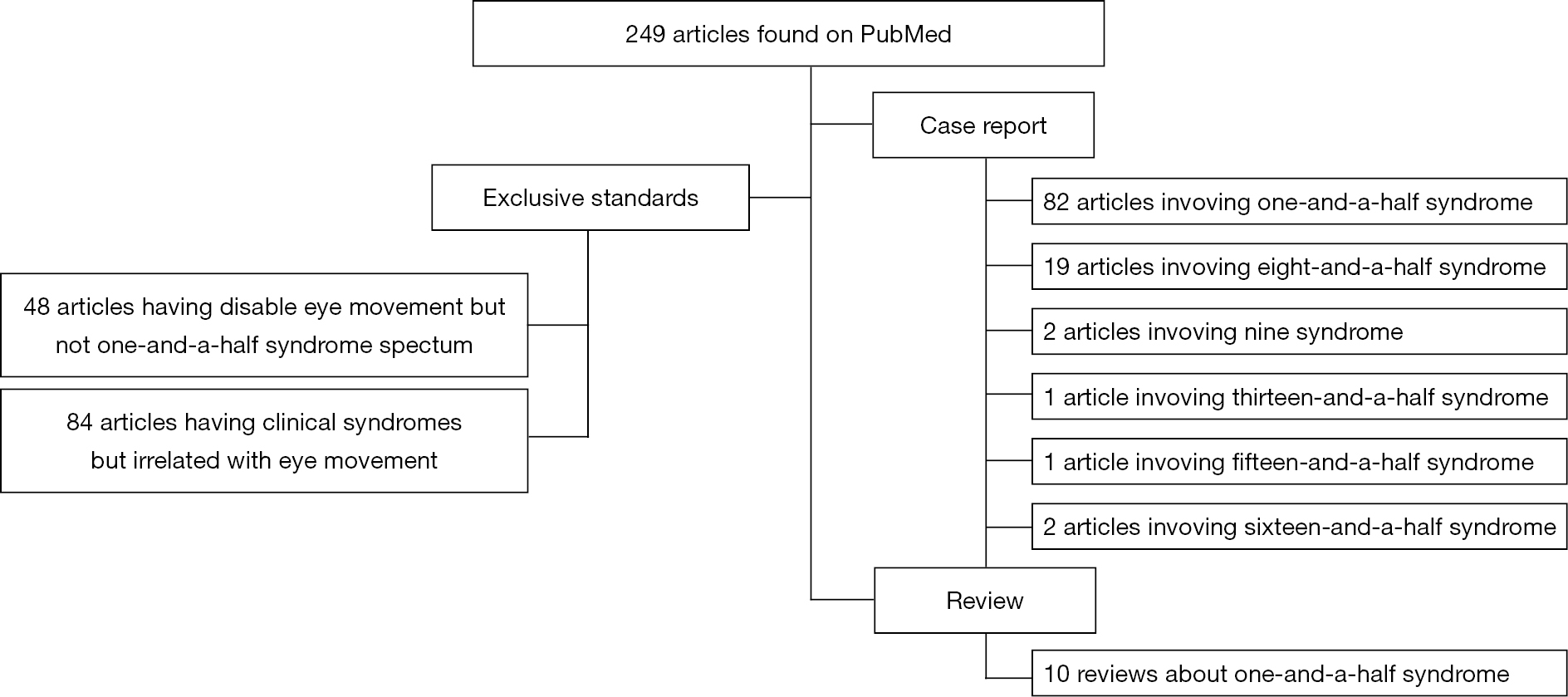
One and a half syndrome is a syndrome characterized by horizontal movement disorders of the eyeballs which was first reported and named by fisher in 1967. The apparent adduction deficits can be overcome with convergence. Clinicians should be aware of the various syndromes that can occur in dorsal and ventral pontine. This article reviews rare cases of one and a half.
Internuclear ophthalmoplegia ino. Internuclear ophthalmoplegia ino is the inability to move both your eyes together when looking to the side. It can affect only one eye or both eyes. More formally it is characterized by a conjugate horizontal gaze palsy in one direction and an internuclear ophthalmoplegia in the other nystagmus is also present when the eye on the opposite side of the lesion is.